Real Estate: Building Foundations for Life, Wealth, and Communities
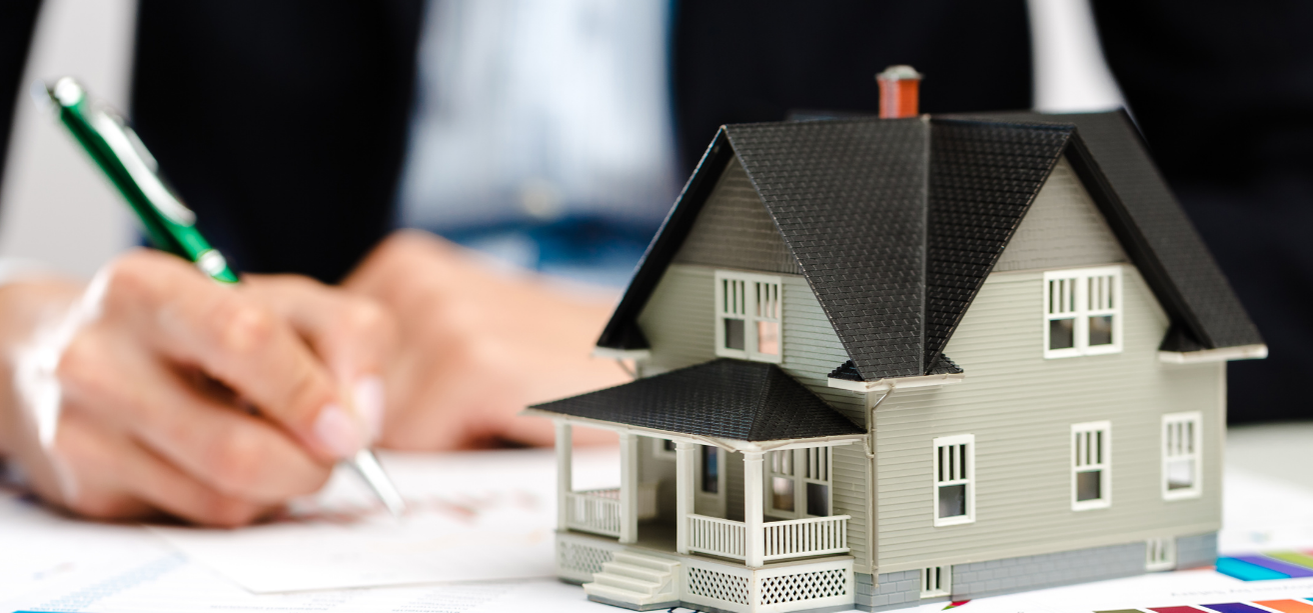
Real estate is one of the most powerful forces shaping our lives and societies. From the home we return to each day to the offices where ideas turn into businesses, real estate defines how we live, work, and grow. It is more than a physical asset—it is a long-term commitment to stability, progress, and opportunity.
Throughout history, land and property have symbolized security and independence. Even today, real estate remains one of the most trusted paths toward financial strength and community development.
Understanding Real Estate
Real estate refers to land and any permanent structures attached to it, including residential homes, commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and undeveloped land. Unlike movable assets, real estate is fixed in location, making its value deeply influenced by surroundings, infrastructure, and economic conditions.
Ownership of real estate carries both rights and responsibilities—the right to use, rent, or sell the property, and the responsibility to maintain and develop it ethically.
Major Categories of Real Estate
Residential Real Estate
Residential real estate includes houses, apartments, condominiums, and residential complexes. A home is often the most significant investment a person makes, representing safety, comfort, and emotional security.
Commercial Real Estate
Commercial real estate encompasses office buildings, retail spaces, hotels, and service centers. These properties support business operations, create employment, and drive economic growth.
Industrial Real Estate
Industrial properties include factories, warehouses, logistics hubs, and manufacturing units. Though less visible, industrial real estate is essential for supply chains, trade, and economic productivity.
Land and Development Property
Land represents pure potential. Whether used for agriculture, housing, or large-scale development, land is the foundation upon which cities and infrastructure are built.
Real Estate as a Long-Term Investment
- Long-term capital appreciation
- Regular rental income
- Protection against inflation
- Tangible asset ownership
Social and Economic Impact
Real estate directly affects economic growth, employment, and social welfare. Responsible development prioritizes sustainability, inclusivity, and environmental balance.
Real Estate in the Digital Age
Online property listings, virtual tours, digital contracts, and smart building technologies have increased transparency and efficiency.
Challenges
Rising property prices, overcrowding, environmental impact, and regulatory complexity require ethical planning and strong governance.
Conclusion
Real estate is not just about ownership—it is about legacy. It shapes skylines, supports economies, and provides spaces where lives unfold.
View Property Details